

The telescope's construction and initial operation were managed by NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory, with Ball Aerospace responsible for developing the Kepler flight system. The Kepler space telescope was part of NASA's Discovery Program of relatively low-cost science missions.
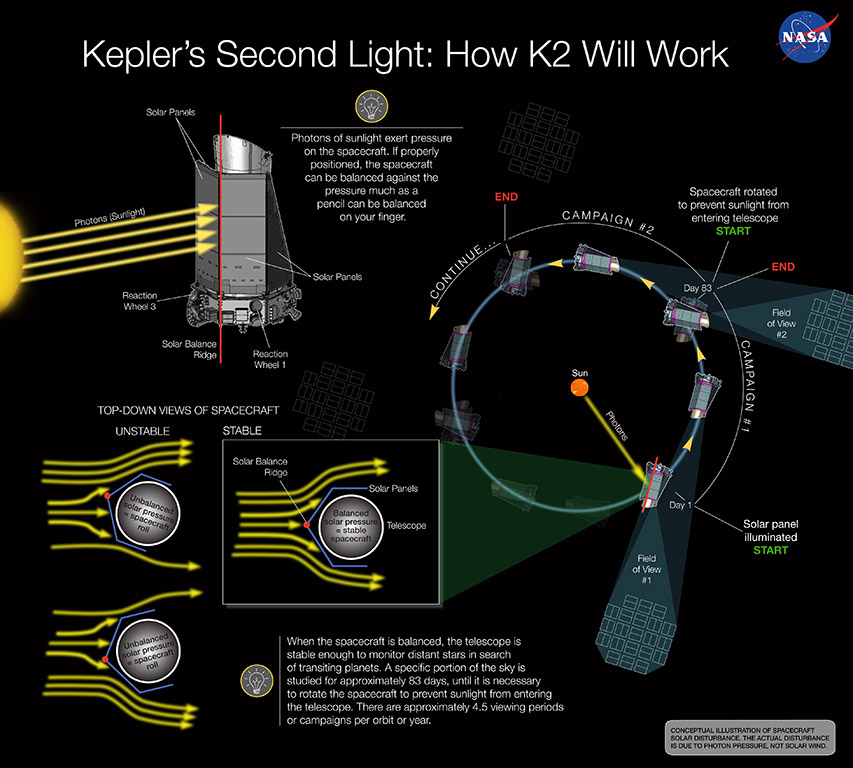
Kepler observed 530,506 stars and detected 2,778 confirmed planets as of June 16, 2023. Only planets whose orbits are seen edge-on from Earth could be detected. These data were transmitted to Earth, then analyzed to detect periodic dimming caused by exoplanets that cross in front of their host star. ĭesigned to survey a portion of Earth's region of the Milky Way to discover Earth-size exoplanets in or near habitable zones and estimate how many of the billions of stars in the Milky Way have such planets, Kepler's sole scientific instrument is a photometer that continually monitored the brightness of approximately 150,000 main sequence stars in a fixed field of view. After nine and a half years of operation, the telescope's reaction control system fuel was depleted, and NASA announced its retirement on October 30, 2018. The principal investigator was William J. Named after astronomer Johannes Kepler, the spacecraft was launched into an Earth-trailing heliocentric orbit. The Kepler space telescope is a disused space telescope launched by NASA in 2009 to discover Earth-sized planets orbiting other stars. Artist's impression of the Kepler telescope


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
